How To Plant Bamboo
Knowing how to plant bamboo correctly, will help you establish a healthier crop and improved productivity on your bamboo farm or plantation. The distance between the plants will determine what size bamboo poles you may expect in the future.
Spacing between Bamboo Plants
The spacing between bamboo plants will depend on the species to be planted, the primary goal of the plantation, and local soil and climate conditions.
The size and physical dimensions of the bamboo species to be planted is an important factor to determine the planting density. Higher densities (closer spacing) are suitable for smaller-sized bamboos, and lower densities (more spaced out) are suitable for larger-sized bamboos.
If the bamboo plants are spaced too far apart, the plantation will suffer from canopy exposure, loss of soil moisture through evaporation, and competition from weeds and other vegetation. An excessively dense plantation will lead to bamboo plants competing amongst themselves for light, space, soil moisture and nutrients.
When you know how to plant bamboo, the plantation will have a steady stream of culm production. The following spacing guidelines may be followed:
Spacing Between Bamboo Plants
For medium-diameter, thick-walled species, 5 x 5 meters spacing is optimal. This requires 400 clumps per hectare, or 160 clumps per acre. This spacing is good for species such as Guadua angustifolia, Dendrocalamus asper and Dendrocalamus brandisii. Under well-managed conditions it can go up to 6 x 6 or 7 x 7 meters.
For smaller species, 4 x 4 meters spacing will be sufficient. This requires 625 plants per hectare.
For larger species, such ass Dendrocalamus hamiltonii, the spacing can be 7 x 7 meters, or 205 plants per hectare. For Dendrocalamus giganteus this can even go up to 10 x 10 meters, or 100 plants per hectare.
Smaller 3 x 3 meters spacing (1,100 plants per hectare) will also work, if the primary goal is soil stabilization.
If the objective is to plant bamboo for erosion control along riverbanks or to protect an area from landslides and avalanches, the spacing can also be 3 x 3 meters or even 2.5 x 2.5 meters. In such cases, bamboo can be mixed together with appropriate, fast-growing timber species as well.
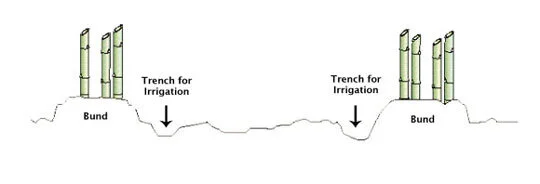
How to Plant Bamboo with the Bund and Trench Method
The bund and trench method involves digging trenches and heaping the dug out soil in order to plant bamboo on 1 meter wide and 50 centimeter high bunds.
Bund and Trench Planting Method
Bunds and trenches should be prepared well in advance to stabilize them before planting the bamboo.
The bund and trench method has several advantages. Bamboo planted on bunds with a base of well-worked soil, turned over from the trenches, will thrive. In the following years, more soil can be dug out of the trenches and heaped or mounded around the bamboo clumps. The trenches can also be used for irrigation, or for preparing organic compost.
How to Plant Bamboo by Triangular Spacing?
For commercial bamboo timber plantations, staggered planting in a triangular grid is recommended. This involves digging pits in alternating rows in the same line, with the row in the middle consisting of pits placed at the center point of the preceding row.
Triangular Bamboo Plant Spacing
This allows for optimal exploitation of the plantation area, and maximizes the distribution space available to each bamboo clump. It also guarantees an equal distance between rows of plants, which can be used for intercropping and organic composting production, and allows for easy passage.
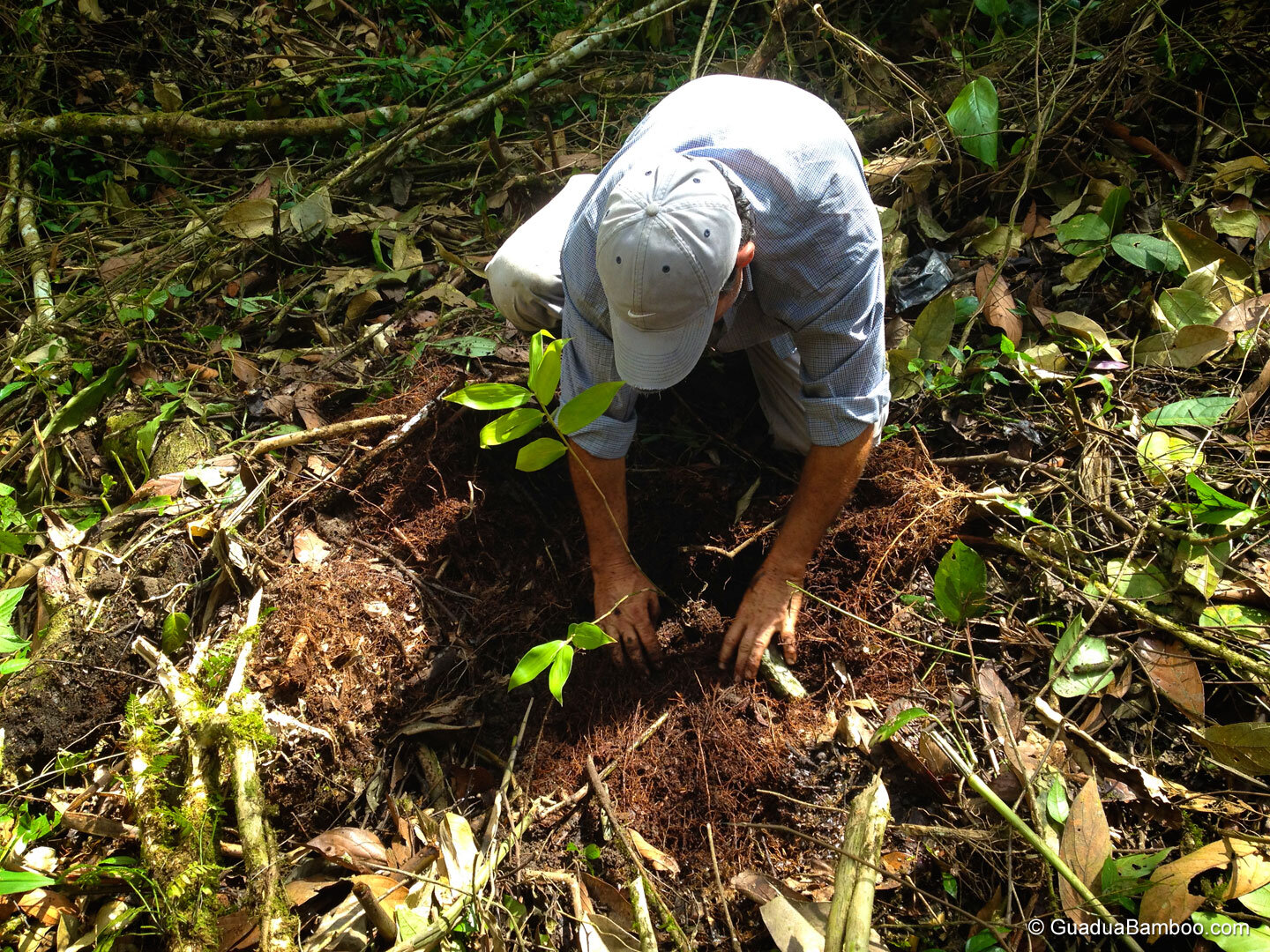
How to Plant Bamboo in Pits?
After clearing the land and before digging the pits, the bamboo plantation area should be measured and marked with sticks from the point that will be the center of the pit.
The pit should be wide and deep enough to ensure that the roots of the bamboo plants have sufficient space, and are not restrained in their search for moisture and nutrients. It is best to prepare the pits before rainy season, and the dug out soil exposed to weather conditions.
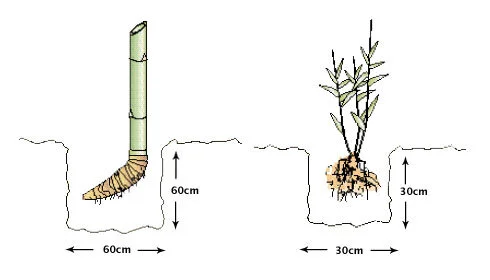
Pit Size for Planting Bamboo
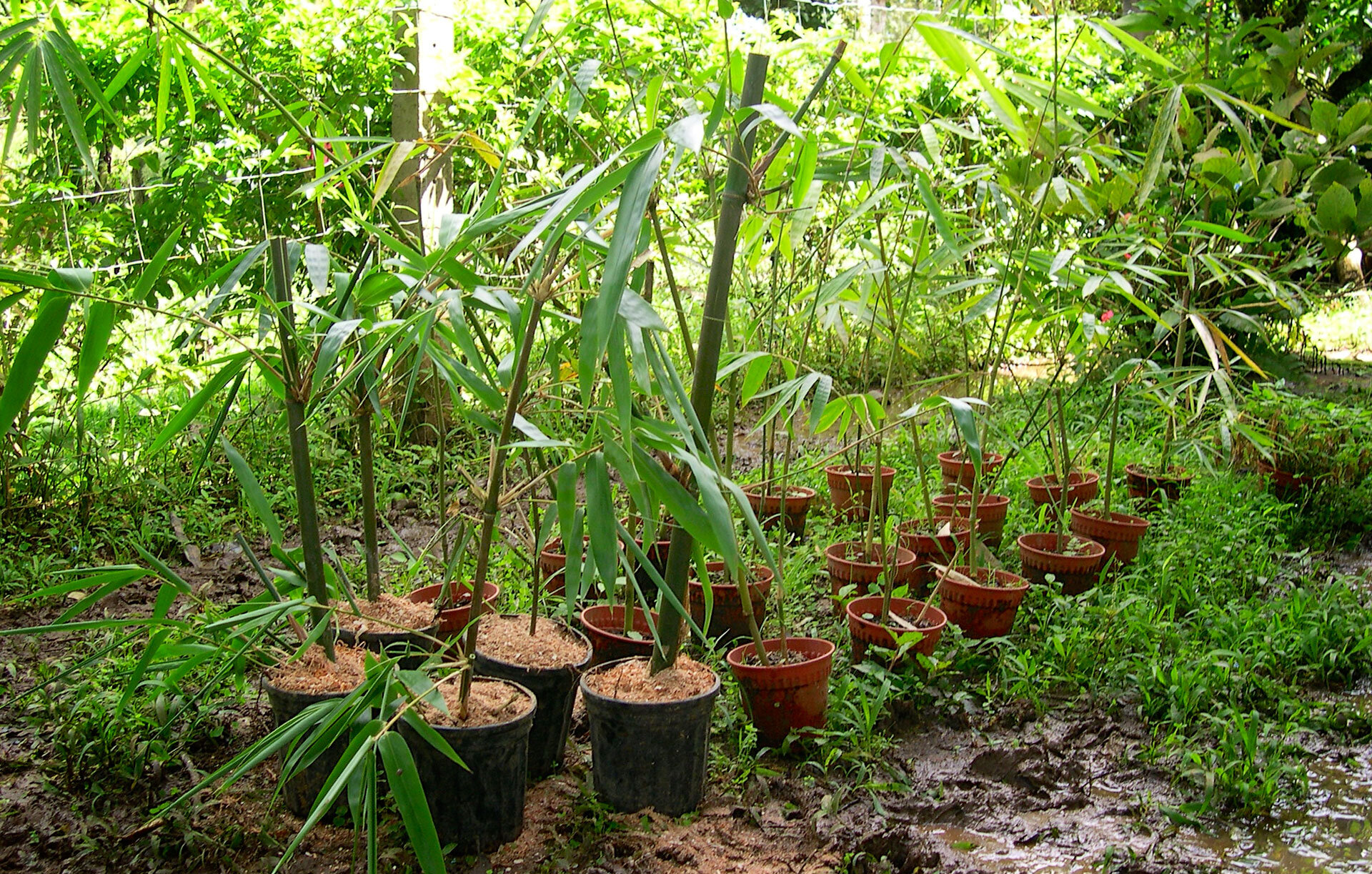
As a rule of thumb rule: the larger the pit, the better the growth of the rhizomes. Offsets and rhizomes should be planted in pits measuring 60 x 60 x 60 to 100 x 100 x 100 centimeters. For seedlings and branch cuttings, the size can be reduced to 30 x 30 x 30 or 45 x 45 x 45 centimeters.
How to plant bamboo in pits:
A few days before planting, thoroughly turn the soil in the pit.
Remove competing weeds and vegetation within a radius of 50 centimeters around the pit.
For a pit size of 60 x 60 x 60 centimeters, mix the soil with approximately 5 kilograms of farmyard manure (FYM), 100 grams urea, 100 grams super phosphate, and 50 grams muriate of potash. Nitrogen in the ammonium form increases water uptake, resulting in faster growth.
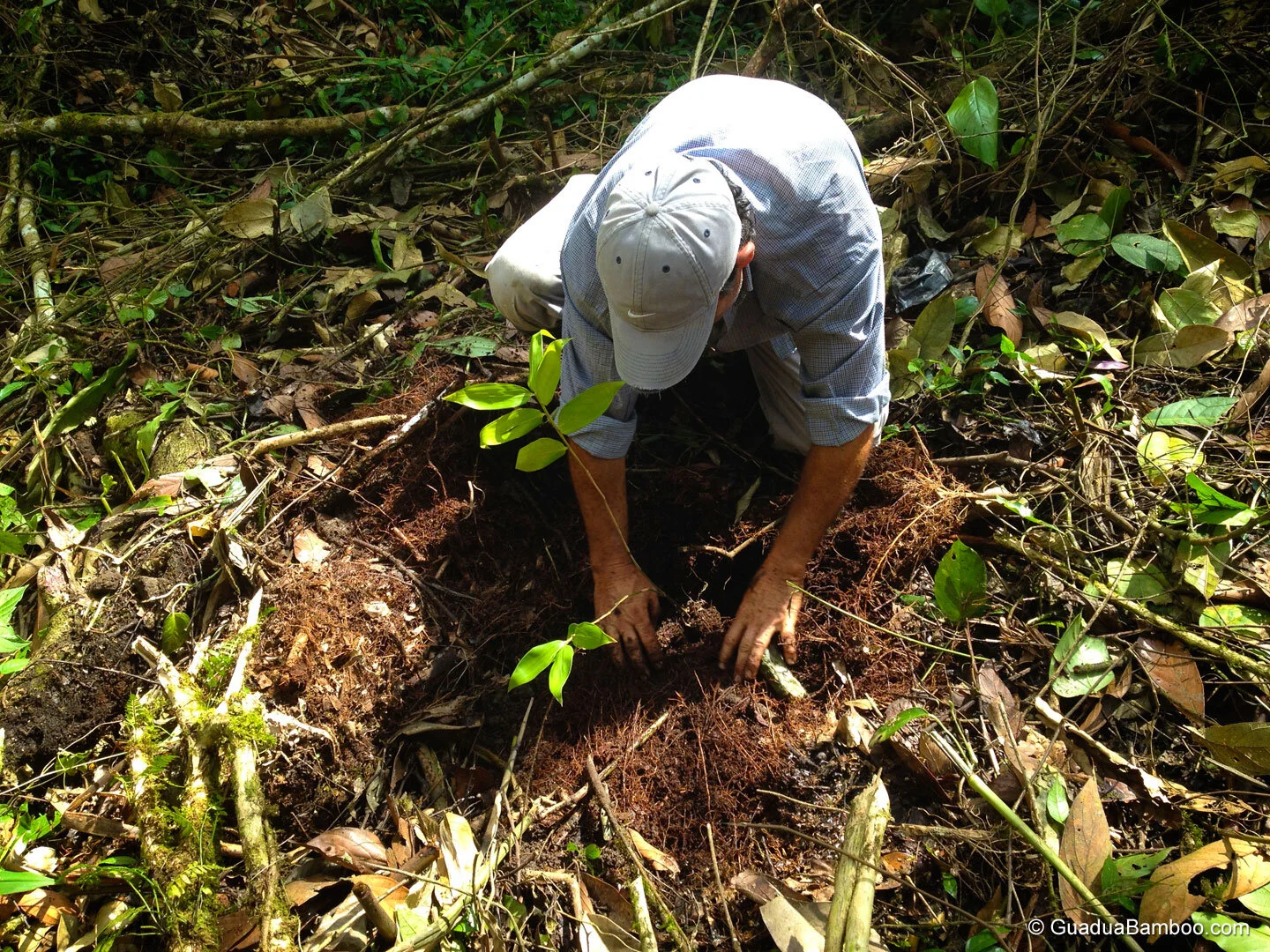
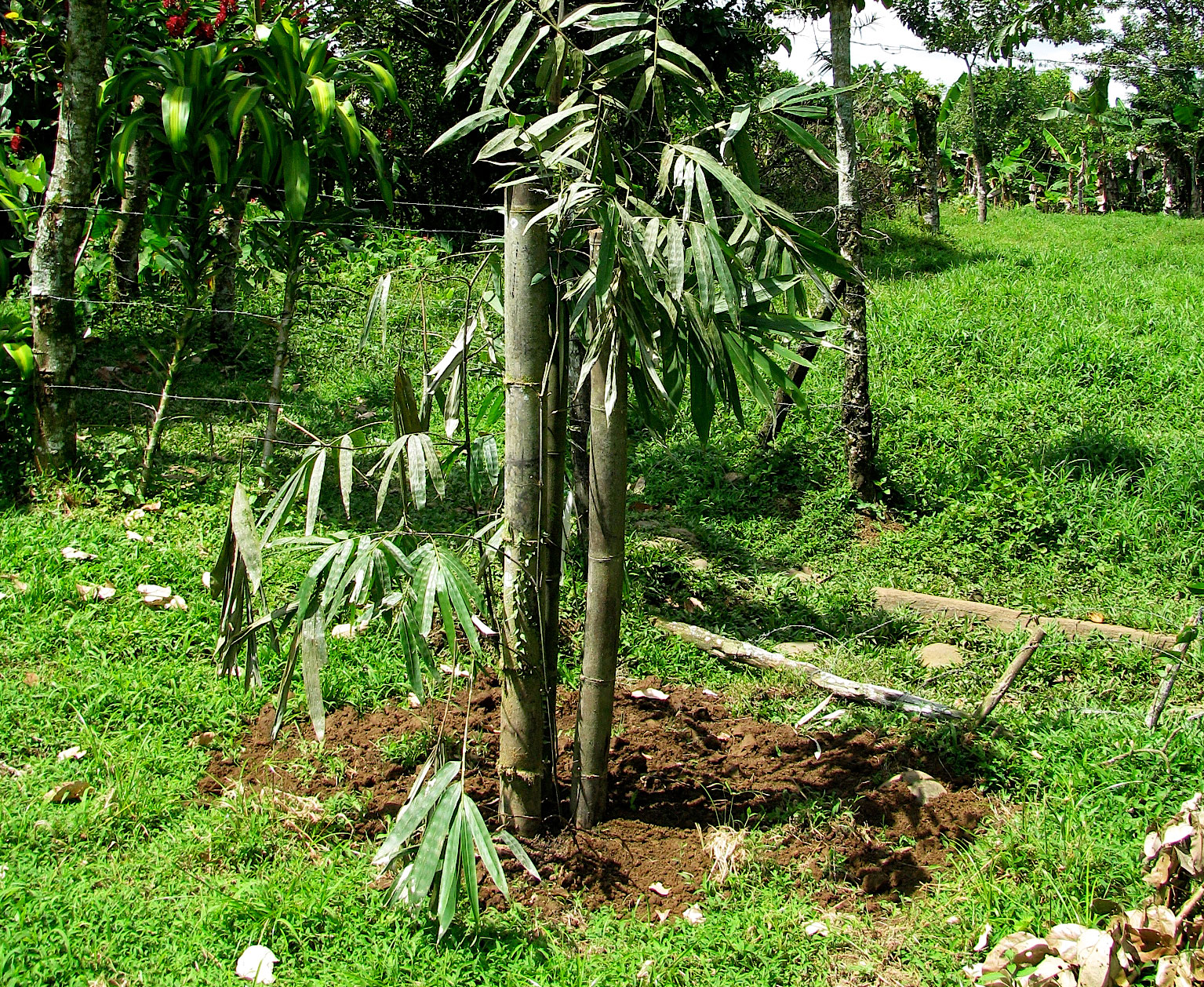
Place the plant vertically in the pit, ensuring that the roots do not curl.
Level the pit with the mixed and enriched soil.
After planting, irrigate with 12–20 liters of water, depending on the current climatic conditions. This will provide the needed moisture to the rhizome and roots, and compress the loose soil around the plant.
Repeat the watering the next day, moderating the quantity of water if necessary. For the next 10 weeks, continue to irrigate if there is not enough rain, initially at daily intervals, extending later to once in three days.















We are planning to plant about an acre of Guadua bamboo seedlings on our land on Ometepe Island, Nicaragua. We will need to irrigate through the dry season for the first and possibly the second year. I am currently evaluating my options for irrigation and would appreciate any feedback.